- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录180 > 2938604 (Phoenix Contact)PWR SUPPLY 10A 100-240AC 24DC
QUINT-PS-100-240AC/24DC/10
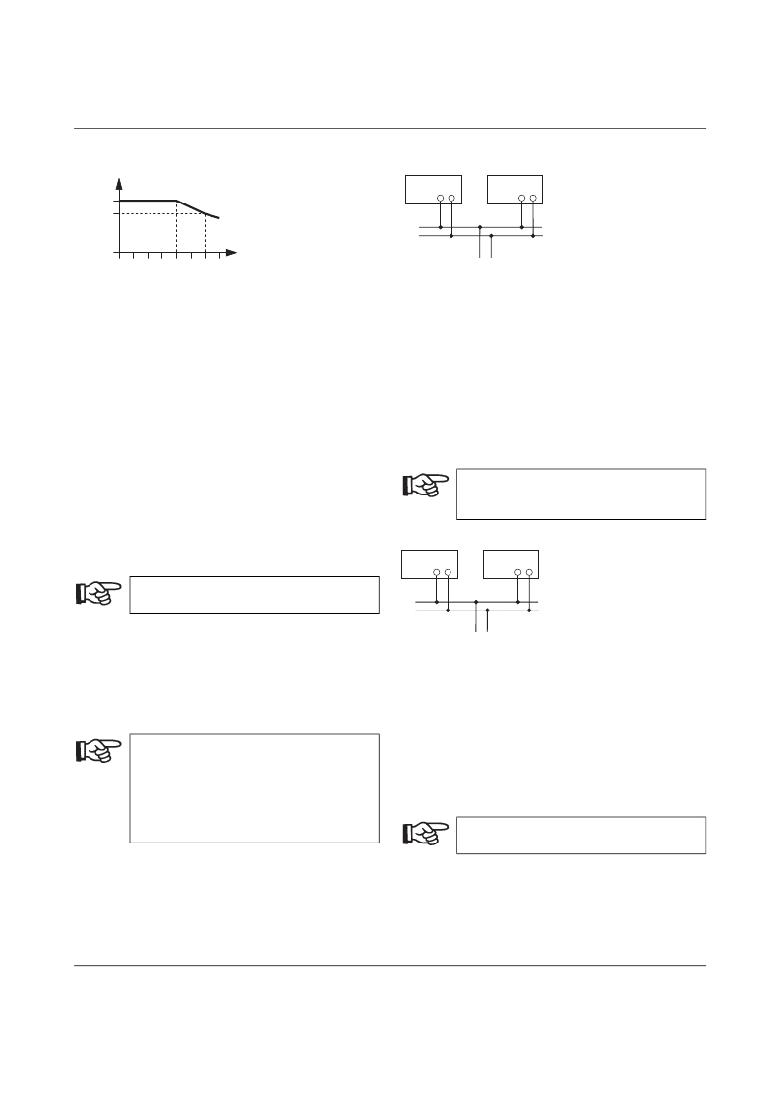
Temperature Response
Redundancy Operation
I BOOST
I N
I N
+ -
I N
+ -
+ -
+ -
0
0 20 40 60
Ambient operating temperature [ ° C]
Figure 14
Temperature response
Figure 15
Σ = I N
Redundancy operation
Redundant circuits are suitable for supplying systems,
At an ambient operating temperature of up to +40 ° C, the
device continuously supplies the I BOOST output current.
The device can supply a nominal output current of I N up to
an ambient operating temperature of +60 ° C. The output
power must be decreased by 2.5% per Kelvin temperature
increase for ambient operating temperatures over +60 ° C.
At ambient operating temperatures above +70 ° C or in the
event of a thermal overload, the device does not switch off.
The output power is decreased to such an extent that
device protection is provided. Once the device has cooled
down, the output power is increased again.
Parallel Operation
which place particularly high demands on operational
safety.
If a fault occurs in the primary circuit of the first power
supply unit, the second device automatically takes over the
entire power supply, without interruption, and vice versa.
For this purpose, the power supply units to be connected in
parallel must be large enough that the total current
requirements of all loads can be fully met by one power
supply unit.
External decoupling diodes are required for
100% redundancy
(QUINT-DIODE/40, Order No. 29 38 96 3).
+ -
Devices of the same type can be connected in parallel to
increase both redundancy and power. The default setting
does not have to be adjusted.
A maximum of five devices can be connected
in parallel.
If the output voltage is adjusted, an even current distribution
can be ensured by precisely setting all power supply units
Increasing Power
I N I N
+ -
+ -
+ -
Σ = 2 * I N
that are operated in parallel to the same output voltage.
To ensure symmetrical current distribution we recommend
Figure 16
Increasing power
that all cable connections from the power supply unit to the
DIN rail are the same length and have the same cross
section.
Depending on the system, for parallel
connection of more than two power supply
units a protective circuit should be installed at
each individual device output (e.g., decoupling
diode or DC fuse). This prevents high return
currents in the event of a secondary device
fault.
? PHOENIX CONTACT 12/2005
The output current can be increased to n x I N where n is the
number of devices connected in parallel.
Parallel connection for increasing power is used when
extending existing systems. A parallel connection is
recommended if the power supply unit does not cover the
current consumption of the most powerful load.
Otherwise, the loads should be divided over independent
individual devices.
A maximum of five devices can be connected
in parallel.
100030_04_en
PHOENIX CONTACT
11
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
2938617
POWR SUPPLY 10A 3X400-500AC 24DC
2938620
PWR SUPPLY 20A 100-240AC 24DC
2938633
POWER SUPPLY 30A 24VDC
2938646
POWR SUPPLY 40A 3X400-500AC 24DC
2938714
PWR SUPPLY 3A 100-240AC 5DC
2938727
POWR SUPPLY 20A 3X400-500AC 24DC
2938730
PWR SUPPLY 2A 100-240AC 24VDC
2938743
POWER SUPPLY 1A 2X15VDC
相关代理商/技术参数
29-3861
制造商:AIM Cambridge Connectivity Solutions 功能描述:
2938617
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 QUINT 3PHASE 24V 10A
RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
29-3861P
制造商:AIM Cambridge Connectivity Solutions 功能描述:
2938620
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 QUINT 24V 20.0A
RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
2938633
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 QUINT 3PHASE 24V 30A
RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
29-3863P
制造商:AIM Cambridge Connectivity Solutions 功能描述:
2938646
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 QUINT 3PHASE 24V 40A
RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
29-3864P
制造商:AIM Cambridge Connectivity Solutions 功能描述:
